A few months ago, Joel discovered a fascinating book that he shared with all of us on the team. The title of the book was “The Decision Maker” and it proposed a radically different idea to how companies are run.
In short, it put traditional management on its head. Instead of higher-ups making decisions, often far removed from the real problems that team members face, you give the decision making power to those that are closest to the problem.
Implementing this has been an incredible transformation of Buffer as a company. Here is how we have implemented this across our whole team a few weeks ago:
Our new setup at Buffer
As a 24-person team, we have very recently split out into various product teams. Each of these teams is completely autonomous, makes their own decisions, and sets their own goals and schedule.
We have 6 product areas at Buffer currently:
- Onboarding
- Buffer for Android
- Buffer for iOS
- Browser Extensions
- Buffer Dashboard + the Awesome plan
- Buffer for Business
The way we build product is that each of these teams has 4 stages that need to be completed for a successful feature release or experiment:
- Growth = What are our intriguing numbers we can pursue to grow Buffer?
- Research = What are our customers biggest problems (in the area of our intriguing numbers)?
- Product = How can we solve this problem in the most efficient and useful way?
- Tech = How can we implement this problem efficiently and successfully for our customers?
Each of these 4 areas needs to make substantial decisions for a new feature to be useful. We have 1 person per area that is completely independent in answering the above question for them. Here is an example of a team that works on the Buffer dashboard:
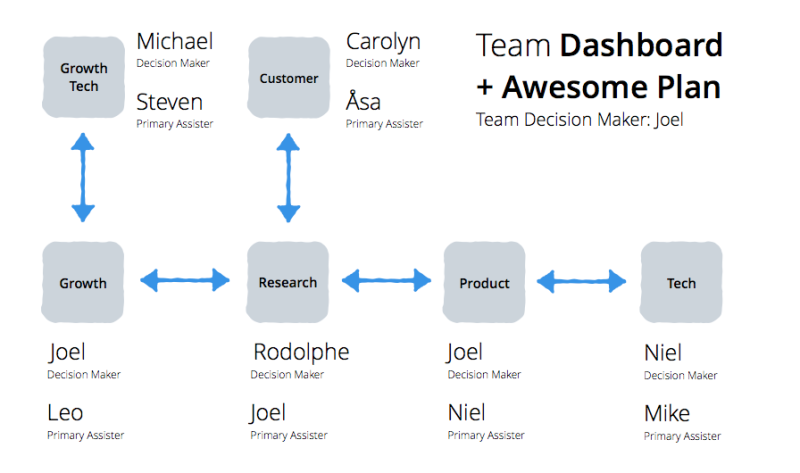
An example scenario of how we might work together
In an example scenario, Joel might discover an intriguing number by analyzing our data. On the dashboard, we found that some of the most common actions are changing your posting schedule, however we also know that the schedule tab causes some of the most confusion with the product.
Having identified that number, Joel passes it along to Rodolphe, who then does customers development with customers on the schedule tab. How are we causing them confusion? What problems do they have when it comes to scheduling their social media posts?
Rodolphe then presents the problem he discovered as clearly as possible to the product person with a validated hypothesis. Example “If we improve the schedule tab, then more customers will stay actively using Buffer, due to our research showing that the current confusion of how timing works causes drop-off.”
Rodolphe would also loop in “Customer”, in this case Carolyn, to see if around the intriguing number we might have already learned something from support requests so far. This is especially helpful to cut down research time and also know about the emotional state of a customer about a problem, which can help with prioritizing it better.
Joel sketches and specs an iteration of how our social scheduling tab might work. Once he’s done, he might pass it back to Rodolphe to clarify with some customers whether we are actually solving their problems.
Once we’re positive on that, we’ll pass the finished spec to the tech decision maker. They will then go ahead and decide how to best implement the new solution and roll it out to our customers.
There is no one person that “runs” this process; it’s a combined effort of decisions for each and every area.
A natural question might be, how can you make sure that the decision each person makes is a good one? A crucial element of the decision maker concept is the advice process. Here is how it works.
The most important part for our change: The advice process
Without managers, how can we ensure we’re still making sound decisions? Quite simply, by asking for advice. The advice process is one of the hardest things to get right and something we place special importance on.
In general, the larger a decision, the more people you might ask for advice. If you want to build a whole new product, you might want to speak with every single person of the company and get their advice. For smaller decision, it’s ideal to speak with fewer people and for some, possibly with no one.
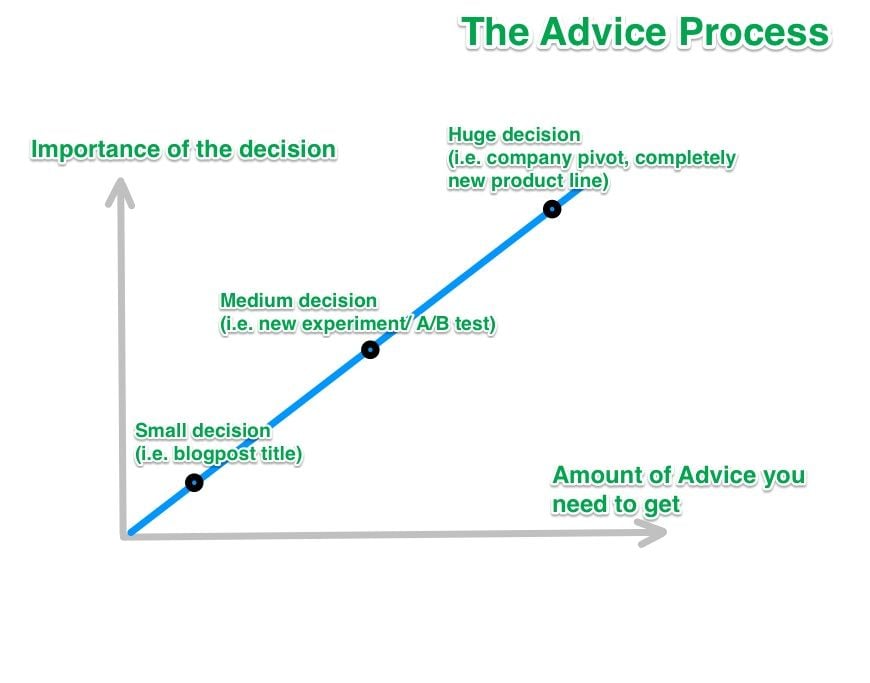
The way we’re thinking about advice is to avoid a top-down approach. Someone from the growth team might get advice from someone else doing growth on a different team, on top of getting advice from leaders in the company. On “research,” for example, getting advice from the happiness team is crucial, as well as from the marketing team, since Buffer is a marketing product and our marketing team is likely the best user of our own product.
The advice process is so important that Bakke went as far as saying:
“the worst trouble you’ll get into won’t be for making a mistake. It’ll be for not asking for advice. Like I said, asking for the advice will help keep you out of trouble.”
So, in our above example, if the person owning “Growth” decides to pass along an intriguing number to “Research”, which is effectively a big decision, as it’ll affect the work of the rest of the team, she is required to get advice on her decision. This can be a short conversation with another person owning “Growth” in a different area, or an otherwise experienced leader that might have a good intuition on a decision.
Sidenote for founders and executives: One of our investors, Dharmesh Shah pointed out that this gets particularly hard as a founder: You need to be able to give people advice, with the real option that they might not take it and go a different route—and you have to be fine with it. All things considered, I believe this might have been one of the hardest things for me to do so far. Whereas before your word as a leader or manager might have been the definite way to go, it is now only one piece of the decision maker framework. While my ego gets in the way at times, it always makes me feel incredibly hopeful to being able to scale this company very far, whenever this happens.
Some current limitations and things we are aiming to improve
As you will see from the above formation diagram, Joel is filling 2 roles right now for the Dashboard team, serving as both the owner of “Growth” and “Product.” That is certainly a challenge and can lead to stretching yourself too thin, and is something we’re actively trying to improve (we’re hiring btw, check out our open positions here! :)
We also have some people that are part of multiple teams, which makes this even harder, yet it’s of course all part of the plan when you’re a startup.
Another thing that I personally struggle with a lot is that it’s often not that obvious when you’re actually making a big decision. Being self-aware and at times going a tiny bit slower than you’d like can substantially improve the decision making of everyone in your company. I expect that this might take a bit of time as we are all getting fully familiar with the new concept.
Scaling a company where everyone enjoys their work
Although we are convinced that the decision maker framework is the most efficient and productive way to run a company, this isn’t necessarily the root of this change. At the very heart lies the idea of giving people control. Dennis Bakke writes that:
“Only if we’re in control, we can have fun doing what we do.”
That was also why Joel and I started Buffer in the first place – to have complete freedom for how we work and what we decided to do with our lives. A few years into working on Buffer, although we personally have achieved that vision, we haven’t extended this to the rest of the team. The decision maker framework is an opportunity to give the whole company the same amount of freedom that we feel.
I believe it’s also allowing us to make better decisions that will create a better product for our nearly 2 million customers. (Ready to save time with social media while driving more traffic and engagement? Try Buffer for free!)
I remember a Tweet from Danielle Morill once where she asked, “will there ever be a 1,000 person company who people really and genuinely enjoy working for more than anything else?” With the limited knowledge that I have, I believe that the decision maker framework might have something to do with the answer to that question.
How do decisions get made where you are? I would love your thoughts on our slightly crazy new way of working as a company and what you’ve found to work well within your workplace!
Interested in joining us on our journey? We’re hiring!
Try Buffer for free
190,000+ creators, small businesses, and marketers use Buffer to grow their audiences every month.



